Lidar – what the iPhone laser can do
No time right now?
What exactly is lidar and what is supposed to be so revolutionary about it? A potential analysis shows how the iPhone laser allows smartphone users to measure distances flexibly.
Lidar is an abbreviation and stands for “Light Detection and Ranging”. Radar-like technology has been used to scan and map environments since the 1960s. Unlike radar, lidar does not use radio waves, but laser beams to measure distances.
Initially, the technology was used for military purposes in aircraft. Lidar became famous when the system was used in the 1970s for the Apollo 15 mission to map the surface of the moon. Since then, the systems have become smaller, cheaper and more precise – and are now a good addition to mobile devices.
Contents
How does the lidar scanner work?
The lidar system, which is built into the two Pro versions of the iPhone 12 as well as the iPad Pro 2020, scans its surroundings by firing a series of laser pulses at different parts of a scene over a short period of time. This measures the time it takes for the light emitted by the laser to hit an object and return. The light particles reflected from the object not only calculate the distance, but also depict an almost exact copy of the object.
In contrast to “scannerless” systems that create 3D images with the help of a single infrared light pulse, the laser pulses of the lidar scanner not only enable an increase in the range of up to five meters, but also better object occlusion. This means that virtual objects can be hidden behind real objects. This means that lidar technology belongs to the type of “time of flight” sensors that have so far been used in smartphones primarily to improve artificial photo effects such as augmented reality.
What can I do with the lidar scanner?
The lidar scanner has so far been designed primarily for space-related applications, such as for various measuring tape, furniture or shopping applications. Some users should already be familiar with these functions from the technically somewhat inaccurate AR apps.
But has this already reached its zenith for this technology? With which application scenarios can the technology be connected so that added value is created in addition to the “digital tape measure”? In the following we take a look at different use cases that could be implemented in both the private and the industrial sector. We want to test both the theoretical and the practical potential of the sensor in the smartphone.
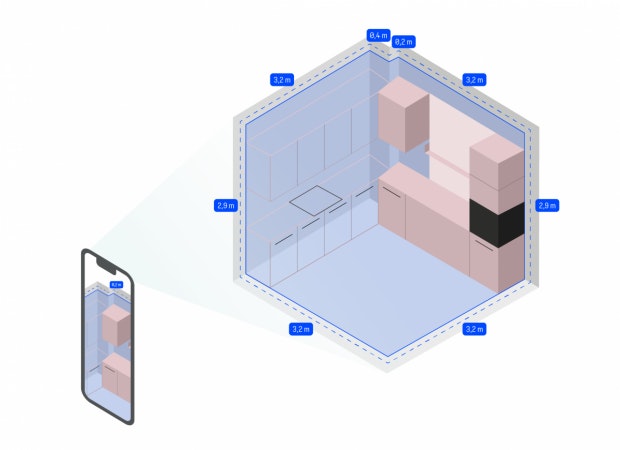
Wall and room measurement
Let us first take a look at the already mentioned, most common area of application of the lidar sensor in applications: wall and room measurement. Elevations or recesses are precisely recognized and easily deducted from the recorded area.
The data and information obtained in this way can be used, for example, to plan a kitchen that is optimally adapted to the room. In this way, the lidar sensor can help to use the available space on the walls effectively.
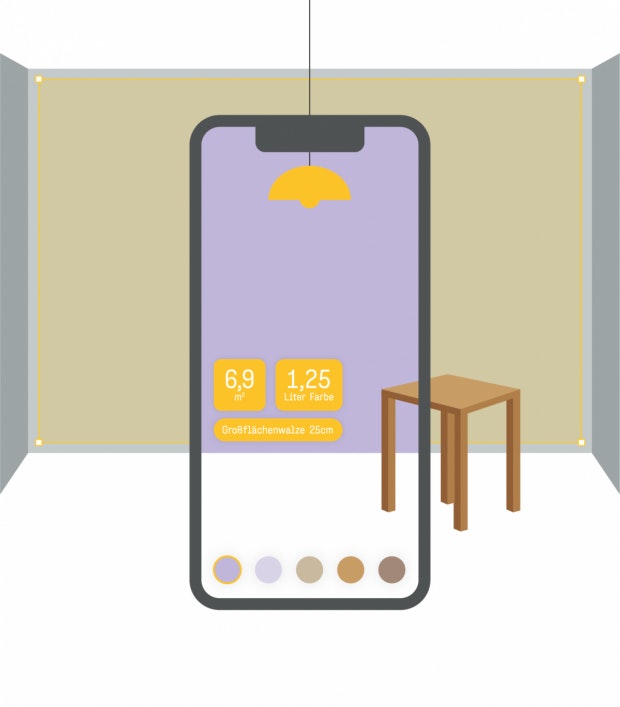
Wall design
Lidar can enable a number of useful functions, especially when designing interiors: It would be conceivable that users could: use their smartphone sensor to measure a room or a wall inside. The calculated area of the wall in square meters is then displayed, as well as any paint consumption and a recommended tool for painting. At the same time, it is possible to test different colors for the wall live. Objects in front of the wall are recognized and easily deducted from the projected color surface.
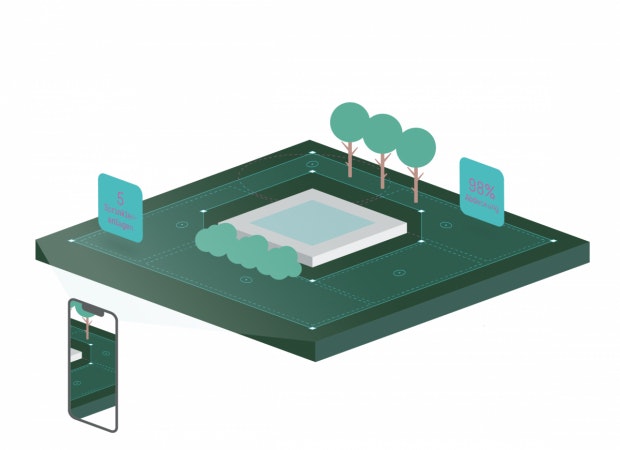
Garden surveying
Since the lidar sensor can be used both indoors and outdoors, it can also be used to support garden maintenance. Application scenarios such as specifically planned garden irrigation or control of a robot lawn mower are possible here. First you measure the garden with the help of the lidar sensor and mark out an area in which you want to mow or water. The sensor also provides information about the soil properties and obstacles, which enables the robotic lawnmower to react accordingly.
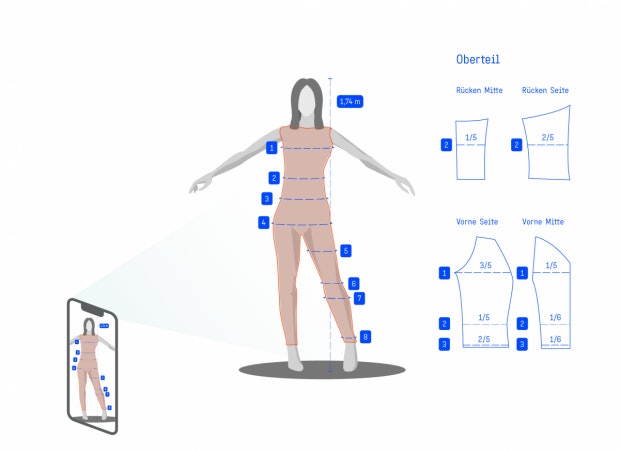
Body measurement
In the textile and fashion industry, too, the lidar sensor can be wonderfully integrated into common work processes together with the iPhone or iPad. Garments can be perfectly adapted and tailored with the help of a previously made 3D model of your own body. Pinching jeans or sleeves that are too short are a thing of the past.
As can be seen from the use cases, the lidar sensor can be used in both private and commercial environments. The fast, precise measurement and further processing of the measured values result in many different forms of application.
But the success of these applications seems to be closely related to the accuracy of scanning objects, rooms and people.
Research & Development with Lidar
In order to assess the feasibility of these ideas and their challenges, we have developed a test application with which we can check the measured values of the lidar sensor.
To do this, we carried out limit tests in which the test app on the iPhone 12 Pro uses the lidar sensor to measure the distance between the device itself and an object in the room. The measured values that the lidar sensor delivers depend, among other things, on the targeted surface. Depending on the nature of the surface, it can happen that the values are less precise (see table: Accuracy) and deviate from the actual distance (ground truth) to the object.
Also interesting: The first iPad with laser – iPad Pro 2020 tested
In addition to distance measurement by aiming at a point, the test application also offers the option of placing a virtual object in the real world and measuring the distance between the device and the fixed virtual object – even when the device is in motion. This type of measurement uses the AR kit’s Raycast method. This method checks whether and where in the real world surfaces exist in order to enter there place virtual object to be able to. If a surface was found and the virtual object could be positioned, the distance to the device is calculated based on this object. In the following table we have evaluated a selection of measurement results from the two methods (iPad Lidar without and with Raycast) against the actual distance.
The results show that the lidar sensor can calculate well to very well within five meters. At distances of less than 14 centimeters, however, the measurement results are too imprecise, so that a measurement error cannot be ruled out.
| Units in m | ||||||
| Surface | Accuracy | Ground truth | iPad LiDAR | Error LiDAR | iPad LiDAR Raycast | Error LiDAR Raycast |
| Gray floor | Low accuracy | 0.02 | 0.05 | -0.03 | Surface could not be detected | |
| Gray floor | High accuracy | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.14 | 0 |
| Concrete wall | High accuracy | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0 | 0.22 | 0 |
| White wall | High accuracy | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0 | 0.39 | 0 |
| Gray floor | High accuracy | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0 | 0.5 | -0.01 |
| Gray floor | High accuracy | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0 | 0.59 | -0.01 |
| White wall | High accuracy | 1.05 | 1.05 | 0 | 1.08 | -0.03 |
| Window | Low accuracy | 1.05 | 2.6 | -1.55 | Surface could not be detected | |
| Black steel barrel | High accuracy | 1.05 | 1.05 | 0 | 1.08 | -0.03 |
| Blue carpet | High accuracy | 1.05 | 1.05 | 0 | 1.08 | -0.03 |
| Concrete pillar | High accuracy | 1.05 | 1.05 | 0 | 1.08 | -0.03 |
| White wall | High accuracy | 4.68 | 4.68 | 0 | 4.82 | -0.14 |
| White wall | High accuracy | 4.9 | 4.91 | -0.01 | 5.04 | -0.14 |
| White wall | Low accuracy | 5 | 5.1 | -0.1 | Surface could not be detected | |
| White wall | Low accuracy | 5.34 | 5.2 | 0.14 | 5.07 | 0.27 |
Conclusion
Since the first use of the lidar sensor on the Apollo 15 mission on the moon, the technology has developed enormously. We can now find them very small, handy and quick in our mobile devices and can use them indoors and outdoors without any problems. Thanks to the laser beams emitted by the sensor, rooms as well as people, bodies and other shapes can be measured.
For the use cases presented here, the measurement accuracy of the lidar sensor in the iPhone and iPad is more than sufficient. With this, R&D has shown that nothing stands in the way of the success of the technology, which is also influenced by the accuracy of the measurements.
Lidar technology brings the potential for exciting, far-reaching and also lucrative innovations. The availability for a broader target group will give rise to interesting application scenarios and digitize and digitize different specialist areas.




