When the smartphone becomes a disease
People suffering from nomophobia fear being away from their smartphone. Researchers from Göttingen have now published a new study on the anxiety disorder. The results are alarming.
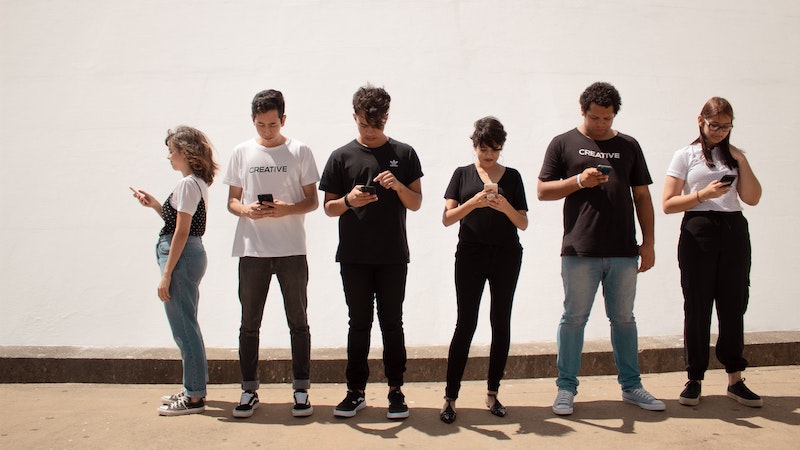
There are hardly any people who do not own a cell phone. Because mobile phones now not only determine our everyday work but also our free time. statistics According to this, around 62.6 million people use a smartphone in Germany alone.
But while mobile devices are helpful in many situations, they also have negative effects. Because if the battery is empty or the smartphone is not in the immediate vicinity, young people in particular react nervously. This feeling can even develop into a full-blown mental disorder: nomophobia.
Contents
What is nomophobia?
The word “nomophobia” is derived from the phrase “no mobile phone phobia”. How among other things National Geographic explains, this refers to the fear of being separated from one’s cell phone and therefore unreachable and cut off from social contacts.
To the symptoms include uncertainty and inner unrest. But tremors, tachycardia and sweating can also occur if those affected cannot use their mobile phone for a longer period of time.
Often behind the actually relatively harmless phenomena is an addictive behavior that requires treatment or another mental illness, report doctors Private clinic Merbeck.
Anxiety disorder widespread in Germany
In Germany, too, nomophobia is more common than previously thought. That recently got a new one study of the Private University of Göttingen (PFH).
The researchers, led by psychology professor Yvonne Görlich, examined the manifestations of the anxiety disorder in Germany for the first time.
Over 800 people took part in nomophobia study
To do this, they interviewed 807 subjects aged around 25. Their smartphone time averaged about four hours and 16 minutes per day.
All participants had to fill out a questionnaire that measured the severity of four factors associated with smartphone withdrawal:
- unable to communicate
- loss of connection
- Unable to access information
- sacrifice of comfort
The questionnaire called Nomophobia Questionaire NMP-Q is used internationally and was translated and validated by the research team in Göttingen.
Nomophobia triggers mental illness
The researchers found that 49.4 percent of the participants had moderate nomophobia. About 4.1 percent of people are even severely affected by the anxiety disorder.
The subjects stated that they felt uncomfortable without their smartphone. They would also get nervous, anxious, and irritable if they had to go without their cell phones.
In addition, the behavior of those tested seems to have negative psychological consequences. Previous studies have found significant associations between nomophobia and loneliness, depression, distraction, and decreased impulse control, Görlich said.
Women more affected than men
The researchers also found that nomophobia is closely linked to the fear of missing out. In addition, women suffer more and more frequently from the anxiety disorder than men.
This was reflected above all in the points “not being able to communicate” and “comfort renunciation”. There, the values of the female respondents were significantly higher. “We can assume that women use the smartphone more for communication due to a greater need for social relationships and thus achieve higher nomophobia scores,” says Görlich.
This is how the researchers want to tackle nomophobia
Another study is currently investigating whether controlled smartphone use can counteract nomophobia. The researchers also want to find out whether this method can also help with symptoms of depression, anxiety and stress.
Within the study, the participants should try smartphone fasting, for example, to control their usage behavior. They also want to observe how controlled use affects people’s well-being.
In this way, those affected can help themselves
If the nomophobia is already more advanced and pronounced, those affected should seek psychological help. However, fixed breaks from the smartphone, digital detox and the conscious distinction between professional life and leisure time could help against initial symptoms.
Breathing and calming exercises also counteract the stress of being available. In addition, meditation, yoga, and progressive muscle relaxation can reduce symptoms of anxiety and stress.
Nomophobia is not yet a recognized mental illness. However, the new study from Göttingen could justify the discussion as to whether the anxiety disorder should not officially belong to the mental illnesses in the future. After all, international studies pointed out loud National Geographic similar results.
Also interesting: