The largest cyclone in the solar system is raging on Jupiter
The cyclone on Jupiter is bigger than the earth. (Image: Shutterstock)
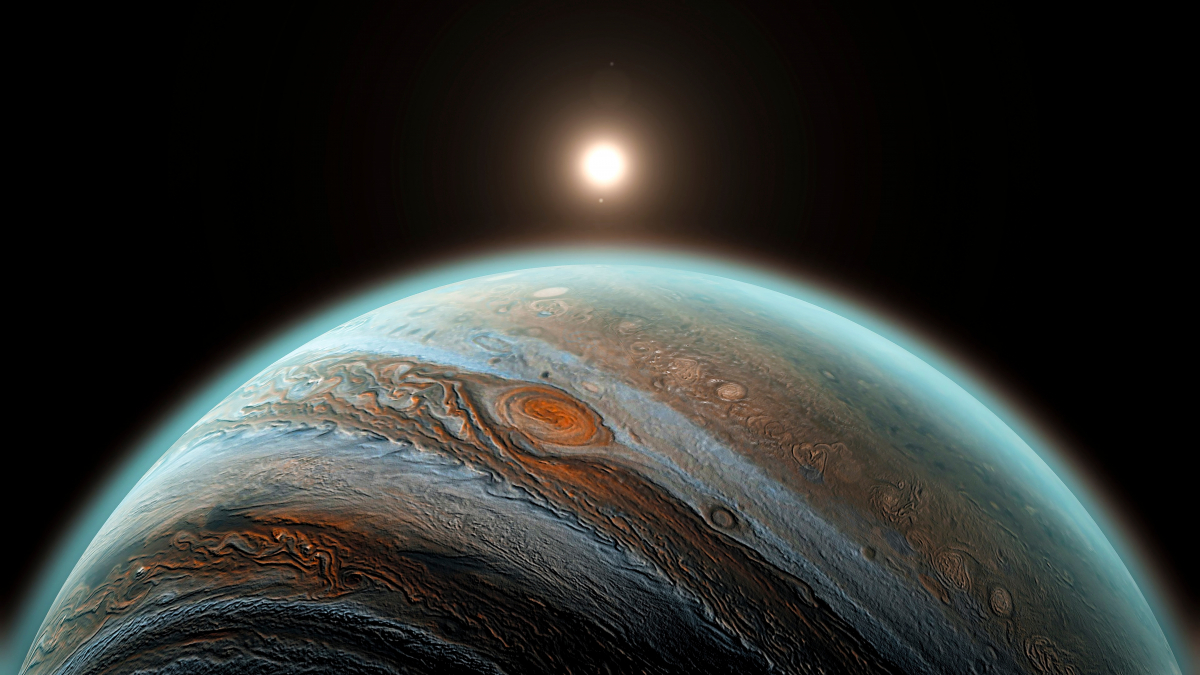
The Great Red Spot of Jupiter is the largest cyclone in the solar system and has existed for over 300 years. Research puzzles why it is getting faster
It is 24,000 kilometers long and 13,000 kilometers wide, making it larger than Earth: the Great Red Spot of the gas giant Jupiter is the largest known cyclone in our solar system. The Italian astronomer Giovanni Domenico Cassini discovered the Great Red Spot as early as the middle of the 17th century. Over the past few decades, the mega-hurricane has changed slightly again and again, from oval to more round and slightly smaller. Now researchers have made a discovery that puzzles them.

Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is speeding up. (Photo: Nasa, Esa, Michael H. Wong / UC Berkeley)
Analysis of data from the Hubble Space Telescope has shown that wind speed in the outer edge of the cyclone increased by up to eight percent between 2009 and 2020. Every year, the cyclone becomes faster by almost 2.5 kilometers per hour. In the meantime, wind speeds of almost 650 kilometers per hour are achieved, like that Nasa announces. These analysis results published Michael Wong’s research team from the University of California at Berkeley in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
When he first saw the results, he wondered if it made sense, Wong said. Something like this has not yet been observed. The exact measurement of the wind speeds of the Great Red Spot is only possible thanks to the data from the Hubble Space Telescope, confirmed NASA researcher Amy Simon, who worked on the study. After all, the changes are so minor that they would not have been noticed without the data spanning eleven years. But it could also be seen that the speeds inside the cyclone had slowed down slightly.
For the researchers, the changes, which at first appear minor, are of great value. Because they could help to understand where the Great Red Spot gets its energy from, what drives it over such a long period of time. Because an external influence, for example from neighboring storms, has not yet been apparent to the observers: inside. Since the Hubble Space Telescope cannot see the bottom of the hurricane, however, finding the cause is complicated for the researchers.