Volvo develops its own operating software VolvoCars.OS and cooperates with Nvidia and Google
The Swedish-Chinese manufacturer Volvo is now also relying on its own expertise for software development. The new Volvocars OS is not intended to be a separate operating system, but rather a framework.
More and more automakers are realizing that the future of the vehicle lies more on the side of the software than that of the hardware. This makes the software substructure a critical factor that can make the difference between success and failure. A company does not leave that to external service providers – at least not exclusively. Tesla has been demonstrating this impressively for over ten years.
It took a while, but now this insight has also reached Volvo. The manufacturer has set up software development in-house and, according to its own statements, is reacting to “the growing importance of software-controlled functions and properties” that are becoming “increasingly important than classic vehicle attributes”.
Contents
Volvocars-OS is an integrative framework
The next generation of Volvo models, including the first SUV on a new technology platform designed exclusively for electric drive, will be based on the Volvocars OS, which the manufacturer defines as the operating system.
The new system should allow faster and more flexible development, which will mean that Volvo cars can be provided with new and optimized features over their entire service life via over-the-air updates. Strictly speaking, this is not an operating system, but rather a framework that integrates the various operating systems in the car and in the cloud, thus creating a coherent software environment. These operating systems mainly include Android Automotive OS, QNX, AUTOSAR and Linux.
Third-party developers can access vehicle functions via open APIs
Volvo intends to use application programming interfaces (APIs) to keep the system open to third-party developers, who can then contribute their own services and applications. The Extended Vehicle API in particular will give developers access to internal vehicle functions such as sensor data, user interfaces and cloud-based functions such as fleet data – provided the customer wants to grant the required authorizations.
Volvo Technical Director Henrik Green envisions a platform that works like a smartphone and enables the software to be constantly updated. In the course of time, “every Volvo will become even better and more comfortable,” says Green.
In addition to a central software framework, Volvo also wants to centralize the control units in the vehicle and bring them together in a core computer. This new core computing system, which will be used for the first time in a new Volvo model introduced in 2022, will consist of three main computers that work together to process images, use artificial intelligence, infotainment and general tasks support.
Close cooperation with Nvidia and Google
In the classic way, Volvo wants to separate the software and hardware from one another so that both spheres can follow a meaningful pace of innovation independently of one another. Volvo has chosen Nvidia as its partner for this core computing system. For the infotainment system, however, the manufacturer wants to work closely with Google.
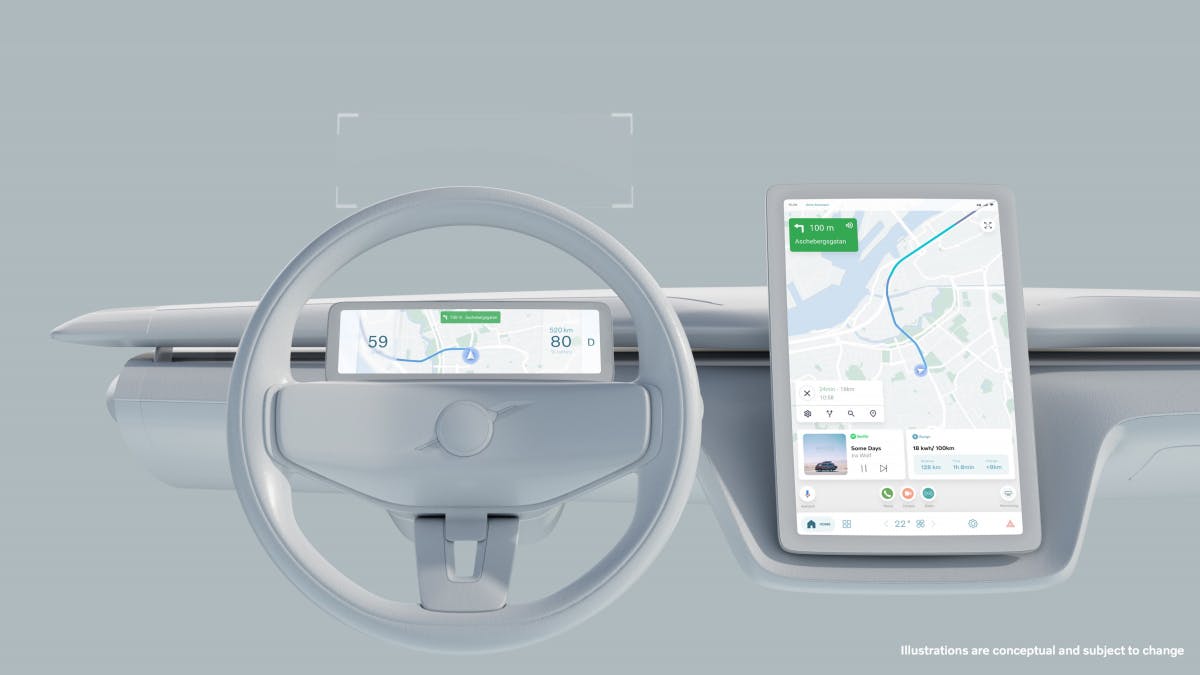
Volvo and Google rely on a comparatively simple and therefore probably safer user experience. A high-resolution driver information display provides all important information such as speed and battery level. An additional head-up display makes it possible to see the most important data without taking your eyes off the road.
In addition, the cooperation partners have provided a large, centrally placed touchscreen. The offers various, also less mission-critical contents, easily recognizable information and allows a familiar interaction by touch or by voice command. The developers avoided deep menu structures. With its minimalistic and context-related approach, the system should provide the relevant and currently required information at the right time.
In addition to the integration of the Android automotive OS, networking with the smartphone plays an important role. The mobile phone should not only serve as a key, but also offer the possibility of controlling many functions. For example, users can pre-air condition their vehicle remotely. The smartphone can also be used to monitor and pay for the charging process. A connection with devices at home is also possible.
“We consciously work with industry leaders where it makes sense,” adds Henrik Green. “Google is a real expert on user experience and services – from Google Maps to the Google Assistant. With Nvidia, in turn, we get access to some of the fastest and best computers. This approach of selected strategic partnerships is much more effective than trying to do it all on your own. “
This approach was unthinkable in the vehicle business just a few years ago. Proprietary technology was seen as the key to success. It remains to be seen to what extent Volvo’s very open approach can prevail over the competition. A few months ago, BMW and Daimler also pursued the approach of joint software development – but then shelved the cooperation.